Atopic Eczema: Understanding the Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Treatments
SEO Meta Description: Are you struggling with Atopic Eczema? Read our comprehensive article to understand the symptoms, causes, and effective treatments for this condition. Get expert insights and helpful tips to manage Atopic Eczema effectively.
Introduction
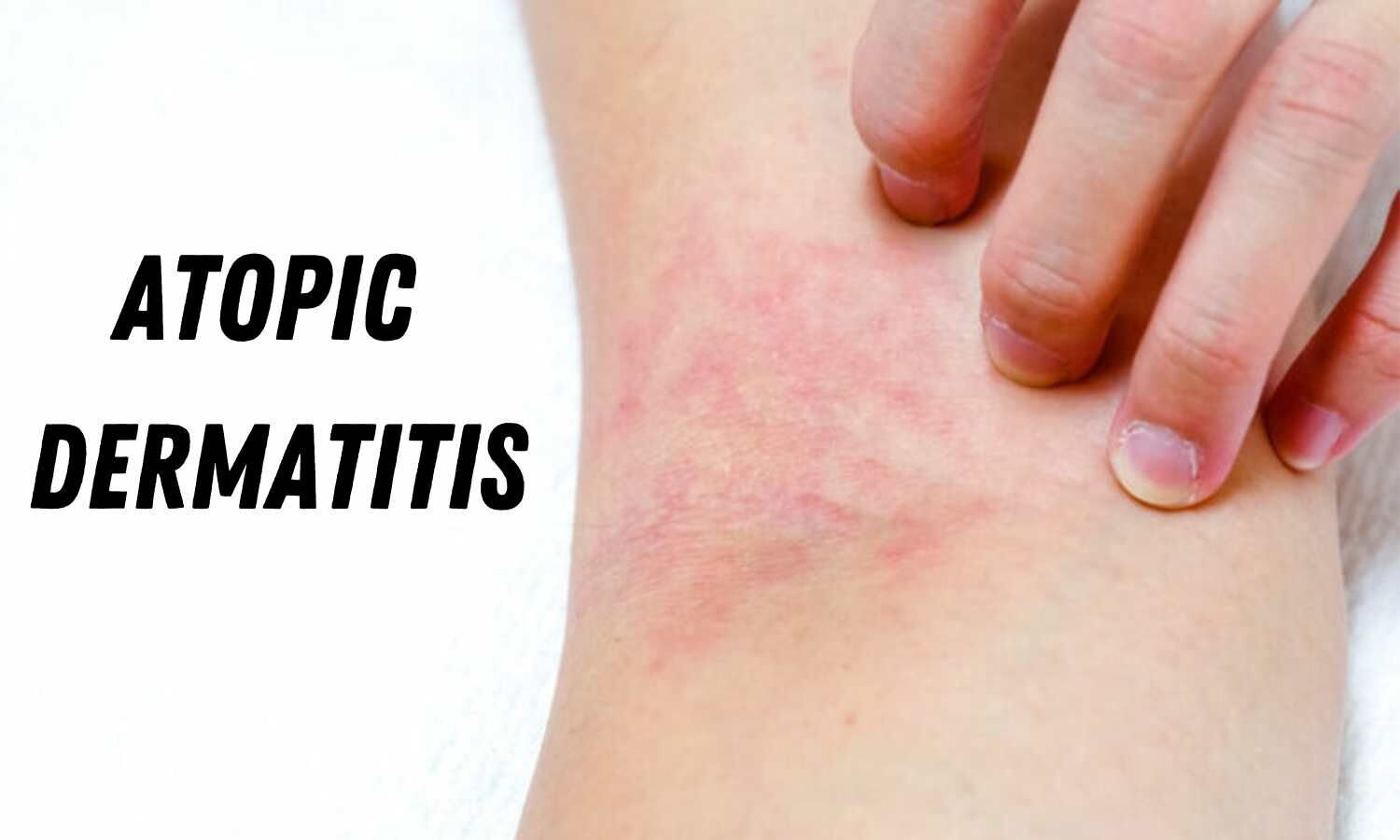
Atopic Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common chronic skin condition characterized by inflamed and itchy skin. It affects millions of people worldwide, and its prevalence has been increasing over the years. In this detailed article, we will explore the ins and outs of Atopic Eczema, covering its symptoms, causes, and various treatment options. Whether you’re experiencing this condition firsthand or seeking knowledge about it, this article aims to provide accurate and relevant information to help you better understand and manage Atopic Eczema.
Atopic Eczema: What is it?
Atopic Eczema is a chronic skin disorder that commonly appears during childhood but can persist into adulthood. It usually involves inflamed, red, and itchy skin patches that can vary in severity. The condition is often associated with other allergic conditions like asthma and hay fever. While the exact cause of Atopic Eczema is not fully understood, a combination of genetic and environmental factors is believed to play a role.
Understanding the Symptoms
The symptoms of Atopic Eczema can vary from mild to severe and may include:
- Itchy Skin: One of the hallmark symptoms of Atopic Eczema is intense itching, which can be particularly bothersome, leading to scratching that worsens the condition.
- Red or Inflamed Skin: Affected areas of the skin may become red, swollen, and inflamed, especially during flare-ups.
- Dry and Sensitive Skin: People with Atopic Eczema often have dry and sensitive skin, making it more susceptible to irritation.
- Bumps or Blisters: In some cases, small raised bumps or fluid-filled blisters may develop on the skin.
- Crusting and Oozing: Scratching the affected skin can lead to crusting and oozing, which can increase the risk of infection.
- Sleep Disturbances: Severe itching can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and decreased quality of life.
What Causes Atopic Eczema?
The exact cause of Atopic Eczema remains unclear, but several factors contribute to its development:
- Genetic Predisposition: Individuals with a family history of Atopic Eczema, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop the condition.
- Abnormal Immune Response: Atopic Eczema is associated with an overactive immune response, leading to inflammation in the skin.
- Skin Barrier Dysfunction: People with Atopic Eczema often have a compromised skin barrier, allowing moisture to escape and irritants to enter.
- Environmental Triggers: Allergens, irritants, and certain weather conditions can trigger or exacerbate Atopic Eczema symptoms.
- Stress: Emotional stress can contribute to flare-ups or worsen existing symptoms.
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis
Diagnosing Atopic Eczema involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and physical examination. There is no specific test to confirm Atopic Eczema, but a healthcare professional may perform a skin biopsy to rule out other skin conditions. Differential diagnosis is crucial to distinguish Atopic Eczema from other skin conditions like contact dermatitis and psoriasis.
Treatment Options
Managing Atopic Eczema involves a multi-faceted approach, which may include:
- Moisturizers: Regularly applying moisturizers helps maintain skin hydration and improve the skin barrier function.
- Topical Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory creams or ointments can effectively reduce redness and itching during flare-ups.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: For milder cases or sensitive areas, these medications may be used as an alternative to corticosteroids.
- Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines can help alleviate itching and improve sleep quality.
- Wet Wrap Therapy: This involves applying wet dressings over affected areas to soothe and hydrate the skin.
- Phototherapy: In some cases, controlled exposure to ultraviolet light can help manage symptoms.
- Immunosuppressants: These medications are reserved for severe cases that don’t respond to other treatments.
- Biologic Therapies: In recent years, biologic medications have shown promise in managing severe Atopic Eczema.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Apart from medical treatments, certain lifestyle changes and home remedies can complement the management of Atopic Eczema:
- Identify Triggers: Keep a journal to identify and avoid triggers that worsen your symptoms.
- Avoid Irritants: Use gentle, fragrance-free skincare products and avoid harsh detergents.
- Maintain Proper Hygiene: Bathe with lukewarm water and pat dry your skin gently.
- Trim Nails: Keep nails short to minimize skin damage from scratching.
- Avoid Hot Baths: Prolonged exposure to hot water can dry out the skin further.
- Use Cotton Clothing: Wear loose-fitting, soft, and breathable cotton clothing to minimize irritation.
Atopic Eczema in Children
Atopic Eczema is common in children, and parents need to take extra care to manage the condition effectively:
- Baby Skincare: Use mild baby skincare products and avoid overdressing the baby.
- Keep Child’s Hands Clean: Teach children not to scratch and keep their hands clean.
- Frequent Moisturization: Regularly moisturize your child’s skin to prevent dryness.
- Talk to the Pediatrician: If you suspect Atopic Eczema in your child, consult a pediatrician for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Coping with Atopic Eczema: Emotional Impact
Living with Atopic Eczema can have a significant emotional toll. It’s essential to address the emotional impact and seek support when needed:
- Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide a sense of community and understanding.
- Counseling: Talking to a mental health professional can help cope with stress and emotional challenges.
- Educate Family and Friends: Educate your loved ones about Atopic Eczema to foster empathy and support.
FAQs
- What triggers Atopic Eczema flare-ups?
- Flare-ups can be triggered by allergens like pollen, pet dander, dust mites, irritants, stress, certain fabrics, and hot weather.
- Is Atopic Eczema Contagious?
- No, Atopic Eczema is not contagious. It’s a non-infectious skin condition.
- Can food allergies worsen Atopic Eczema?
- In some cases, certain food allergies may contribute to the exacerbation of Atopic Eczema symptoms.
- Can adults develop Atopic Eczema for the first time?
- Yes, while Atopic Eczema commonly appears in childhood, it can also develop in adults.
- Can Atopic Eczema be cured?
- Atopic Eczema cannot be cured, but with proper management, symptoms can be controlled effectively.
- Are there alternative therapies for Atopic Eczema?
- Some people find relief with alternative therapies like acupuncture, herbal remedies, or relaxation techniques. However, consult a healthcare professional before trying these.

Conclusion
Atopic Eczema is a challenging skin condition that requires careful management and understanding. By identifying triggers, following a personalized treatment plan, and making lifestyle changes, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. If you suspect Atopic Eczema, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and a tailored treatment approach. Remember, managing Atopic Eczema is a journey, but with the right support and knowledge, it’s possible to lead a fulfilling and itch-free life.
DISCLAIMER:
This information is not presented by a medical practitioner and is for educational and informational purposes only. The content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare providers with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read.
Since natural and/or dietary supplements are not FDA-approved they must be accompanied by a two-part disclaimer on the product label: that the statement has not been evaluated by FDA and that the product is not intended to “diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.”